Contact Us
Bank Routing Number
107001481
Bank by Mail/General Mail
PO Box 26458
Kansas City, MO 64196
Deposit Only Mailbox
PO Box 26744
Kansas City, MO 64196
Phone Number
1-877-712-2265
Download our app
Access your
accounts here.
accounts here.

Grab your phone and scan the code to download!
not featured
2025-06-04
Credit
published
4-minute
Scoring Models: How to Calculate VantageScore

-
-
Understanding your credit score is key to making smart financial decisions. It affects major milestones, like purchasing a home, buying a car, and getting the best credit card perks. Among the different credit scoring models, “VantageScore” ranks as one of the most widely used—second only to the leading model. So, what is a VantageScore? And how are VantageScores calculated? Let’s find out!
VantageScore Definition
A VantageScore is a type of credit score that lenders use to evaluate how likely you are to repay debt. It represents your creditworthiness based on your credit report and other activity.
VantageScore was created in 2006 by the three major credit bureaus—Experian, Equifax, and TransUnion—to offer a more consistent scoring model. Many lenders use VantageScores when deciding to approve applications for loans, credit cards, and more.
All VantageScores are credit scores, but not all credit scores are VantageScores. There are other credit scoring models available, like FICO score. And while Vantage and FICO scores are often lumped together, each is different. They are like Coke vs. Pepsi—similar, but with their own formula and flavor.
Something unique to VantageScores is they update more frequently. This means your score reflects recent changes in your credit activity faster than some other scoring models. Because of this, your score can improve quickly—but it can also fall just as fast with careless management.
VantageScore Ranges
Just like FICO, VantageScore is measured on a scale of 300 to 850. The higher your score, the better your credit looks to lenders. However, VantageScore groups the score ranges differently:
- 300 to 600: Poor Credit (Subprime)
- 601 to 660: Fair Credit (Near Prime)
- 661 to 780: Good Credit (Prime)
- 781 to 850: Excellent Credit (Superprime)
A higher VantageScore makes it easier to access better financial opportunities, while a lower score signals to lenders that you aren’t a reliable borrower.
How to Calculate My VantageScore
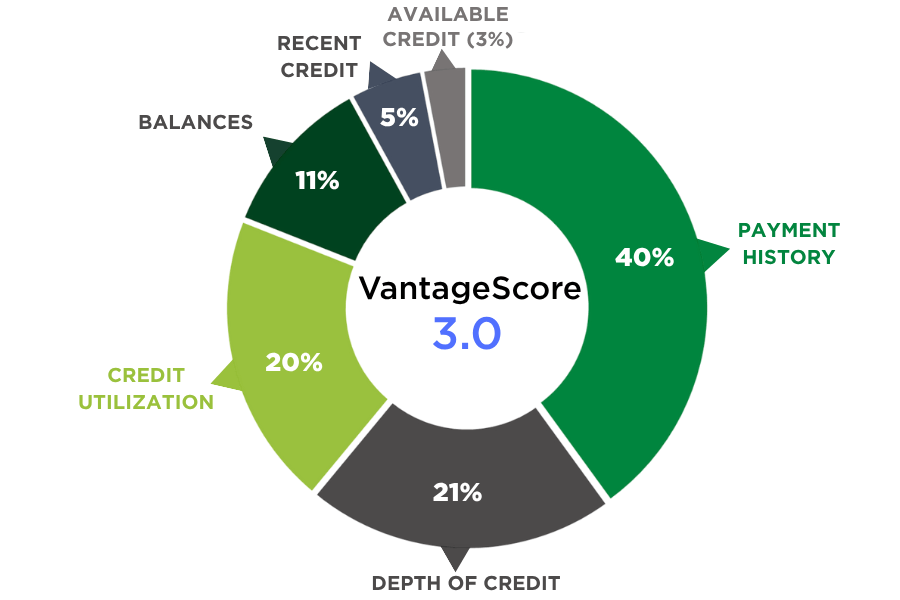
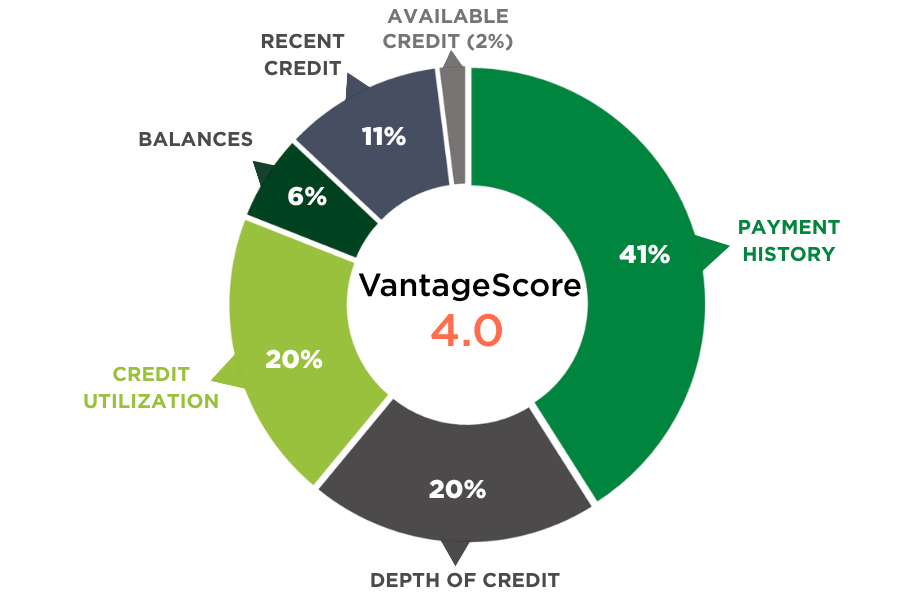
The two main versions of this credit scoring system are VantageScore 3.0 and VantageScore 4.0. While both versions measure the same factors, the weight and importance of each factor is slightly different.
| VantageScore 3.0 | VantageScore 4.0 | |
|---|---|---|
| Payment History | 40% | 41% |
| Depth of Credit | 21% | 20% |
| Credit Utilization | 20% | 20% |
| Balances | 11% | 6% |
| Recent Credit | 5% | 11% |
| Available Credit | 3% | 2% |
So, what does each scoring factor mean? And how does it impact your Vantage credit score? Here’s a closer look:
1. Payment History (40% or 41% of VantageScore)
Your payment history is your record of meeting deadlines for payments. It shows lenders whether you have been a reliable borrower in repaying what you owe on credit cards and loans. Afterall, they need to know if they will get their money back!
- Why Payment History Matters: This is the most influential factor overall. The longer a payment is overdue, the more it will negatively impact your VantageScore.
- Payment History Tip: Always make at least the minimum payment on time—even if it’s just a small amount.
2. Depth of Credit (21% or 20% of VantageScore)
Depth of credit looks at 1) how long your credit accounts have been open; and 2) the variety of credit types you have used—like credit cards, loans, and mortgages. In other scoring models, these two elements separated into “credit history” and “credit mix,” but VantageScore measures them together.
- Why Depth of Credit Matters: A longer, more diverse credit background shows lenders you have experience managing different types of credit.
- Depth of Credit Tip: Don’t close older accounts unless absolutely necessary—open accounts help you develop a longer record that could work in your favor.
3. Credit Utilization (20% of VantageScore)
This measures how much of your available credit you are currently using. For example, if you have a $10,000 credit limit and a $3,000 balance, your utilization ratio is 30%.
- Why Credit Utilization Matters: High utilization can suggest you are overextending yourself, even if you make payments on time. Having a lower utilization shows lenders that you use credit wisely and spend within your means.
- Credit Utilization Tip: Use less than 30% of your total credit, and if possible, aim for 10%. Consider paying your balance more often or raising your credit limit—both options make it easier to keep a good ratio.
4. Balances (11% or 6% of VantageScore)
The balances category looks at the total amount of money you owe across all your credit accounts—both current and delinquent. It shows how much debt you are carrying overall. The impact of balances on your credit score depends on whether the lender pulls from VantageScore 3.0 or 4.0.
- Why Balances Matter: Carrying large balances—even if you pay on time—can indicate financial strain and also hurt your VantageScore.
- Balances Tip: Pay down balances wherever you can to help improve your score. It’s as simple as that!
5. Recent Credit (5% or 11% of VantageScore)
This factor tracks new credit activity—like how many new accounts you open and how many recent credit checks (inquiries) you have made. Recent credit helps lenders gauge how actively you are seeking credit. In the FICO scoring model, recent credit is called “new credit.”
- Why Recent Credit Matters: Applying for multiple credit accounts in a short time is a red flag to lenders because it hints that you are either desperate for money or having financial trouble.
- Recent Credit Tip: Space out credit applications to avoid hurting your VantageScore and improve your chances of getting approved for loans or credit cards.
6. Available Credit (3% or 2% of VantageScore)
Available credit is the amount of credit you have not used by your statement date. It’s the difference between your credit limit and your current balance on revolving accounts like credit cards.
- Why Available Credit Matters: While this has the smallest impact on your VantageScore, having more available credit looks better overall because it shows lenders that you aren’t maxing yourself out.
- Available Credit Tip: Pay off some of your credit balance before the monthly statement date. Also, if you get a credit limit increase, use it wisely. Do not use your increase as a reason to spend more.
Build Credit with a Secured Credit Card
Improving your VantageScore doesn’t happen overnight, but it’s still very important. Afterall, it’s used by lenders to make decisions that impact your financial life. So, if you are wondering where to start, a great choice is applying for a secured credit card! It works like a regular credit card but requires a refundable security deposit, which sets your credit limit. This deposit lowers the lender’s risk, making it easier for you to qualify even if your credit isn’t perfect.
Academy Bank is proud to offer the Credit Builder Secured Credit Card, which is one of the best credit cards for building credit.
Notable Features:
- Set Your Limit: Choose your credit limit (between $300 and $3,000, based on your deposit).
- Automatic Reporting: Your on-time payments and responsible credit activity are reported to the three credit bureaus, helping you build your VantageScore.
- No Hidden Fees: That’s right! No application fees, over-limit fees, and annual fees.
- Path to an Unsecured Card: If you use the Credit Builder Card responsibly, you could qualify for an unsecured credit card in the future (perhaps with perks)!
Academy Bank’s Credit Builder Secured Credit Card offers a simple, practical way to start building or rebuilding credit—without jumping through hoops. Take the first step today!
Need help getting started? Use our Credit Assessment Calculator and other tools to better understand your financial situation.
Subject to credit approval. Transaction and Penalty fees apply. Credit Builder Savings Account required. $300-$3,000 opening deposit required. $5 quarterly fee charged to the Credit Builder Savings Account if not enrolled in eStatements. Improved credit score is not guaranteed. Credit score is determined by credit reporting agencies based on multiple factors, but satisfactory performance on a credit card product can improve your credit score. Default on a credit card, including missed or late payments can damage your credit score. Once added, funds cannot be withdrawn from the Credit Builder Savings Account and the Credit Builder Credit Card without closing the savings account and the credit card.



